Arduino - I2C 通信
I2C 通信是用于微控制器和新一代专用集成电路之间的串行数据交换的系统。当它们之间的距离很短时使用它(接收器和发射器通常在同一印刷板上)。通过两根导线建立连接。一个用于数据传输,另一个用于同步(时钟信号)。
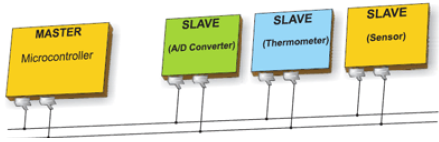
如下图所示,一个设备始终是主设备。它在通信开始之前执行一个从芯片的寻址。这样,一个微控制器就可以与 112 个不同的设备通信。波特率通常为 100 Kb /秒(标准模式)或 10 Kb /秒(慢波特率模式)。最近出现了波特率为 3.4 Mb / sec 的系统。通过 I2C 总线通信的设备之间的距离限制在几米。
板上 I2C 引脚
I2C 总线由两个信号组成 - SCL 和 SDA。SCL 是时钟信号,SDA 是数据信号。当前总线主控器始终生成时钟信号。某些从设备有时可能会强制时钟低电平以延迟主设备发送更多数据(或者在主设备尝试计时之前需要更多时间来准备数据)。这被称为“时钟拉伸”。
以下是不同 Arduino 板的引脚 -
- Uno,Pro Mini - A4(SDA),A5(SCL)
- Due - 20(SDA),21(SCL)
- Leonardo,Cloud 2(SDA),3(SCL)
Arduino I2C
我们有两种模式 - 主代码和从代码 - 使用 I2C 连接两个 Arduino 板。他们是 -
- 主发送器/从接收器
- 主接收器/从发送器
主发送器/从接收器
现在让我们看看主发射器和从接收器是什么。
主发送器
以下函数用于初始化 Wire 库并将 I2C 总线作为主站或从站加入。通常只调用一次。
-
Wire.begin(address)- 在我们的例子中,地址是 7 位从地址,因为未指定主设备,它将作为主设备加入总线。 -
Wire.beginTransmission(address)- 使用给定地址开始传输到 I2C 从设备。 -
Wire.write(value)- 用于从主设备传输到从设备的队列字节(中间调用beginTransmission()和endTransmission()。 -
Wire.endTransmission()- 结束由beginTransmission()启动的从设备的传输,并传输由wire.write()排队的字节。
例
#include <Wire.h> //include wire library
void setup() //this will run only once {
Wire.begin(); // join i2c bus as master
}
short age = 0;
void loop() {
Wire.beginTransmission(2);
// transmit to device #2
Wire.write("age is = ");
Wire.write(age); // sends one byte
Wire.endTransmission(); // stop transmitting
delay(1000);
}
从接收器
使用以下函数 -
-
Wire.begin(address)- 地址是 7 位从机地址。 -
Wire.onReceive(received data handler)- 从设备从主设备接收数据时要调用的函数。 -
Wire.available()- 返回可用Wire.read()检索的字节数。这应该在Wire.onReceive()处理程序中调用。
例
#include <Wire.h> //include wire library
void setup() { //this will run only once
Wire.begin(2); // join i2c bus with address #2
Wire.onReceive(receiveEvent); // call receiveEvent when the master send any thing
Serial.begin(9600); // start serial for output to print what we receive
}
void loop() {
delay(250);
}
//-----this function will execute whenever data is received from master-----//
void receiveEvent(int howMany) {
while (Wire.available()>1) // loop through all but the last {
char c = Wire.read(); // receive byte as a character
Serial.print(c); // print the character
}
}
主接收器/从发送器
现在让我们看看什么是主接收器和从发射器。
主接收器
主机被编程为请求,然后读取从唯一寻址的 Slave Arduino 发送的数据字节。
使用以下函数 -
Wire.requestFrom(address, number of bytes) - 主设备用于从从设备请求字节。然后可以使用函数 wire.available() 和 wire.read() 函数检索字节。
例
#include <Wire.h> //include wire library void setup() {
Wire.begin(); // join i2c bus (address optional for master)
Serial.begin(9600); // start serial for output
}
void loop() {
Wire.requestFrom(2, 1); // request 1 bytes from slave device #2
while (Wire.available()) // slave may send less than requested {
char c = Wire.read(); // receive a byte as character
Serial.print(c); // print the character
}
delay(500);
}
从发送器
使用以下函数。
Wire.onRequest(handler) - 当主设备从此从设备请求数据时,将调用该函数。
例
#include <Wire.h>
void setup() {
Wire.begin(2); // join i2c bus with address #2
Wire.onRequest(requestEvent); // register event
}
Byte x = 0;
void loop() {
delay(100);
}
// function that executes whenever data is requested by master
// this function is registered as an event, see setup()
void requestEvent() {
Wire.write(x); // respond with message of 1 bytes as expected by master
x++;
}