Arduino - 控制语句
决策结构要求程序员指定一个或多个要由程序评估或测试的条件。如果条件被确定为真,则它应与要执行的一个或多个语句一起,并且如果确定条件为假,则应该可选地执行其他语句。
以下是大多数编程语言中的典型决策结构的一般形式 -
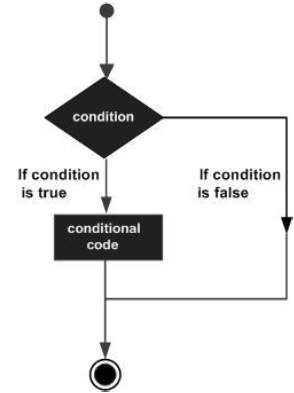
控制语句是源代码中控制程序执行流程的元素。他们是 -
if语句if...else语句if...else if...else语句switch case语句:?条件运算符-三元运算符
if 语句
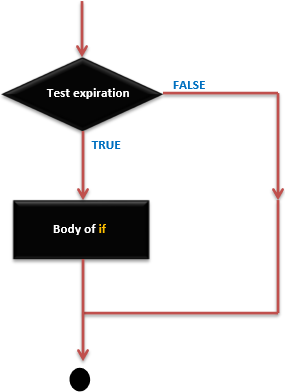
它由括号中的表达式以及语句或语句块组成。如果表达式为 true,则执行语句或语句块,否则将跳过这些语句。
不同形式的 if 语句
形式 1
if (expression)
statement;
如果您有一个语句,则可以使用不带大括号{}的 if 语句。
形式 2
if (expression) {
Block of statements;
}
if 语句 - 执行顺序
举例
/* Global variable definition */
int A = 5 ;
int B = 9 ;
Void setup () {
}
Void loop () {
/* check the boolean condition */
if (A > B) /* if condition is true then execute the following statement*/
A++;
/* check the boolean condition */
If ( ( A < B ) && ( B != 0 )) /* if condition is true then execute the following statement*/ {
A += B;
B--;
}
}
if...else 语句
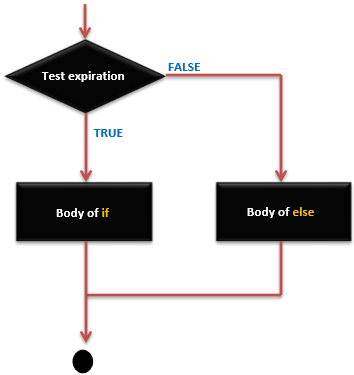
一个 if 语句可以跟着一个可选的 else 语句,当表达式是 false 的,则 else 会被执行。
if … else 语句语法
if (expression) {
Block of statements;
}
else {
Block of statements;
}
if … else 语句 - 执行顺序
举例
/* Global variable definition */
int A = 5 ;
int B = 9 ;
Void setup () {
}
Void loop () {
/* check the boolean condition */
if (A > B) /* if condition is true then execute the following statement*/ {
A++;
}else {
B -= A;
}
}
if...else if...else 语句
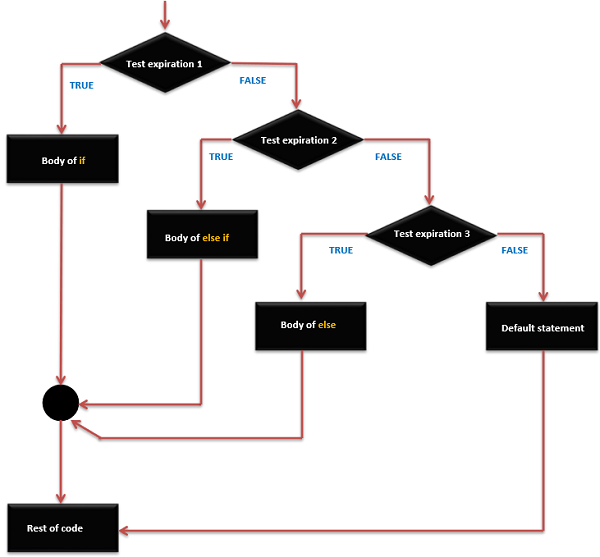
if 语句可以跟着一个可选 else if 语句,这是对有多个条件分支时非常的有用.
当使用 if … else if … else 语句时,请记住 -
- 一个
if可以有零个或一个else语句,它必须在任何其他 if 之后。 - 一个
if能有 0 到多个else if语句,他们必须在else之前。 - 一个
else if为true后,其余的else if或else语句都不会被检测。
if … else if … else 语句语法
if (expression_1) {
Block of statements;
}
else if(expression_2) {
Block of statements;
}
.
.
.
else {
Block of statements;
}
if … else if else else 语句执行顺序
例
/* Global variable definition */
int A = 5 ;
int B = 9 ;
int c = 15;
Void setup () {
}
Void loop () {
/* check the boolean condition */
if (A > B) /* if condition is true then execute the following statement*/ {
A++;
}
/* check the boolean condition */
else if ((A == B )||( B < c) ) /* if condition is true then
execute the following statement*/ {
C = B* A;
}else
c++;
}
switch case 语句
与 if 语句类似,switch … case 通过允许程序员指定应在各种条件下执行的不同代码来控制程序流。特别地,switch 语句将变量的值与 case 语句中指定的值进行比较。 当找到一个 case 语句,其值与变量的值匹配时,将运行该 case 语句中的代码。
break 关键字使得 switch 语句退出,它经常在每个 case 的结尾使用。如果没有 break 语句,switch 语句将继续执行以下表达式直到 break 出现,或者到达 switch 语句的结尾。
switch case 语句语法
switch (variable) {
case label:
// statements
break;
}
case label: {
// statements
break;
}
default: {
// statements
break;
}
switch case 语句执行顺序

举例
这是一个 switch case 的简单示例。假设我们有一个变量阶段,每个状态只有 3 个不同的状态(0,1 或 2)和相应的函数(事件)。这就是我们如何切换状态的代码 -
switch (phase) {
case 0: Lo(); break;
case 1: Mid(); break;
case 2: Hi(); break;
default: Message("Invalid state!");
}
?: 三元条件运算符
条件运算符 ?: 是 C 中唯一的三元运算符。
?: 条件运算符语法
expression1 ? expression2 : expression3
首先评估 expression1。如果其值为 true,则计算 expression2 并忽略 expression3。如果 expression1 为 false,则计算 expression3 并忽略 expression2。运算符结果将是 expression2 或 expression3 的值,具体取决于它们 expression1 是否为 True。
条件运算符从右到左关联。
举例
/* Find max(a, b): */
max = ( a > b ) ? a : b;
/* Convert small letter to capital: */
/* (no parentheses are actually necessary) */
c = ( c >= 'a' && c <= 'z' ) ? ( c - 32 ) : c;
条件算子规则
expression1必须是标量表达式;expression2和expression3必须遵守以下规则之一。expression2和expression3都必须是算术类型。expression2和expression3的结果类型确定。