Arduino - 控制語句
決策結構要求程式設計師指定一個或多個要由程式評估或測試的條件。如果條件被確定為真,則它應與要執行的一個或多個語句一起,並且如果確定條件為假,則應該可選地執行其他語句。
以下是大多數程式語言中的典型決策結構的一般形式 -
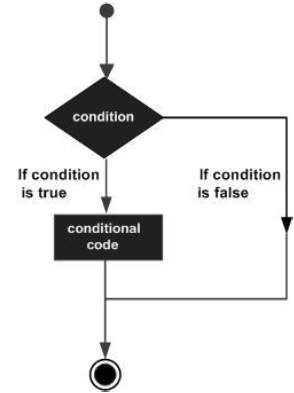
控制語句是原始碼中控制程式執行流程的元素。他們是 -
if語句if...else語句if...else if...else語句switch case語句:?條件運算子-三元運算子
if 語句
它由括號中的表示式以及語句或語句塊組成。如果表示式為 true,則執行語句或語句塊,否則將跳過這些語句。
不同形式的 if 語句
形式 1
if (expression)
statement;
如果您有一個語句,則可以使用不帶大括號{}的 if 語句。
形式 2
if (expression) {
Block of statements;
}
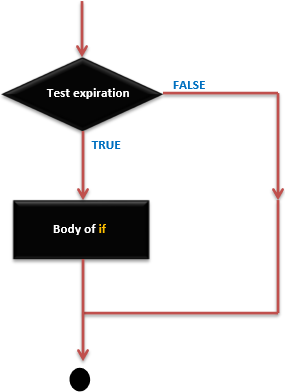
if 語句 - 執行順序
舉例
/* Global variable definition */
int A = 5 ;
int B = 9 ;
Void setup () {
}
Void loop () {
/* check the boolean condition */
if (A > B) /* if condition is true then execute the following statement*/
A++;
/* check the boolean condition */
If ( ( A < B ) && ( B != 0 )) /* if condition is true then execute the following statement*/ {
A += B;
B--;
}
}
if...else 語句
一個 if 語句可以跟著一個可選的 else 語句,當表示式是 false 的,則 else 會被執行。
if … else 語句語法
if (expression) {
Block of statements;
}
else {
Block of statements;
}
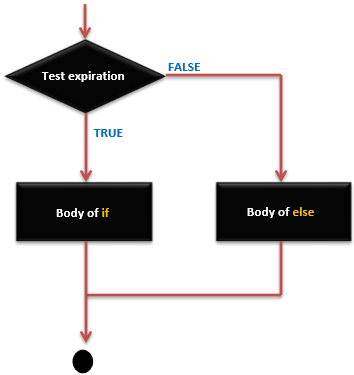
if … else 語句 - 執行順序
舉例
/* Global variable definition */
int A = 5 ;
int B = 9 ;
Void setup () {
}
Void loop () {
/* check the boolean condition */
if (A > B) /* if condition is true then execute the following statement*/ {
A++;
}else {
B -= A;
}
}
if...else if...else 語句
if 語句可以跟著一個可選 else if 語句,這是對有多個條件分支時非常的有用.
當使用 if … else if … else 語句時,請記住 -
- 一個
if可以有零個或一個else語句,它必須在任何其他 if 之後。 - 一個
if能有 0 到多個else if語句,他們必須在else之前。 - 一個
else if為true後,其餘的else if或else語句都不會被檢測。
if … else if … else 語句語法
if (expression_1) {
Block of statements;
}
else if(expression_2) {
Block of statements;
}
.
.
.
else {
Block of statements;
}
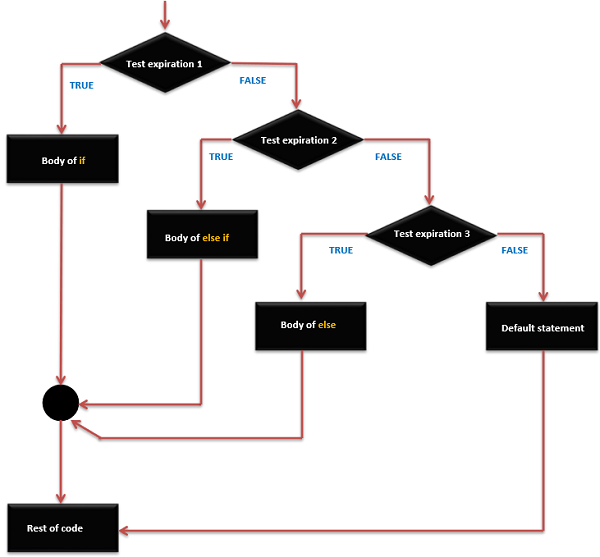
if … else if else else 語句執行順序
例
/* Global variable definition */
int A = 5 ;
int B = 9 ;
int c = 15;
Void setup () {
}
Void loop () {
/* check the boolean condition */
if (A > B) /* if condition is true then execute the following statement*/ {
A++;
}
/* check the boolean condition */
else if ((A == B )||( B < c) ) /* if condition is true then
execute the following statement*/ {
C = B* A;
}else
c++;
}
switch case 語句
與 if 語句類似,switch … case 通過允許程式設計師指定應在各種條件下執行的不同程式碼來控制程式流。特別地,switch 語句將變數的值與 case 語句中指定的值進行比較。 當找到一個 case 語句,其值與變數的值匹配時,將執行該 case 語句中的程式碼。
break 關鍵字使得 switch 語句退出,它經常在每個 case 的結尾使用。如果沒有 break 語句,switch 語句將繼續執行以下表示式直到 break 出現,或者到達 switch 語句的結尾。
switch case 語句語法
switch (variable) {
case label:
// statements
break;
}
case label: {
// statements
break;
}
default: {
// statements
break;
}
switch case 語句執行順序

舉例
這是一個 switch case 的簡單示例。假設我們有一個變數階段,每個狀態只有 3 個不同的狀態(0,1 或 2)和相應的函式(事件)。這就是我們如何切換狀態的程式碼 -
switch (phase) {
case 0: Lo(); break;
case 1: Mid(); break;
case 2: Hi(); break;
default: Message("Invalid state!");
}
?: 三元條件運算子
條件運算子 ?: 是 C 中唯一的三元運算子。
?: 條件運算子語法
expression1 ? expression2 : expression3
首先評估 expression1。如果其值為 true,則計算 expression2 並忽略 expression3。如果 expression1 為 false,則計算 expression3 並忽略 expression2。運算子結果將是 expression2 或 expression3 的值,具體取決於它們 expression1 是否為 True。
條件運算子從右到左關聯。
舉例
/* Find max(a, b): */
max = ( a > b ) ? a : b;
/* Convert small letter to capital: */
/* (no parentheses are actually necessary) */
c = ( c >= 'a' && c <= 'z' ) ? ( c - 32 ) : c;
條件運算元規則
expression1必須是標量表示式;expression2和expression3必須遵守以下規則之一。expression2和expression3都必須是算術型別。expression2和expression3的結果型別確定。