CherryPy - 一个工作应用程序
完整堆栈应用程序提供了通过某些命令或文件执行来创建新应用程序的工具。
考虑像 web2py 框架这样的 Python 应用程序; 整个项目/应用程序是根据 MVC 框架创建的。同样,CherryPy 允许用户根据需要设置和配置代码的布局。
在本章中,我们将详细了解如何创建 CherryPy 应用程序并执行它。
文件系统
该应用程序的文件系统显示在以下屏幕截图中 -
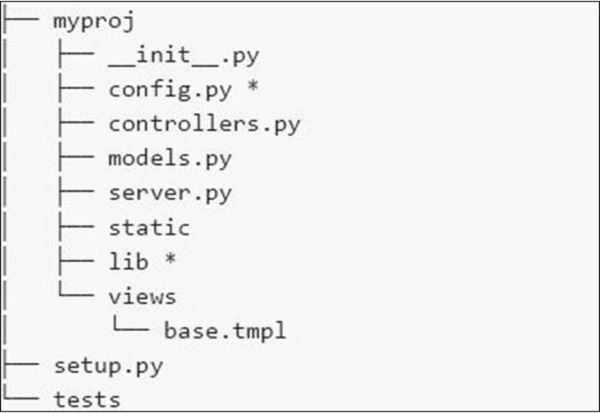
以下是我们在文件系统中拥有的各种文件的简要说明 -
-
config.py- 每个应用程序都需要配置文件和加载它的方法。可以在 config.py 中定义此功能。 -
controllers.py- MVC 是用户遵循的流行设计模式。controllers.py 是实现将安装在 cherrypy.tree 上的所有对象的地方。 -
models.py- 此文件直接与数据库交互以获取某些服务或存储持久数据。 -
server.py- 此文件与生产就绪的 Web 服务器交互,该服务器可与负载平衡代理正常工作。 -
static- 它包含所有 CSS 和图像文件。 -
views- 它包含给定应用程序的所有模板文件。
例
让我们详细了解创建 CherryPy 应用程序的步骤。
步骤 1 - 创建应包含应用程序的应用程序。
步骤 2 - 在目录中,创建一个与项目对应的 python 包。创建 gedit 目录并在其中包含_init_.py 文件。
步骤 3 - 在包内,包含具有以下内容的 controllers.py 文件 -
#!/usr/bin/env python
import cherrypy
class Root(object):
def __init__(self, data):
self.data = data
@cherrypy.expose
def index(self):
return 'Hi! Welcome to your application'
def main(filename):
data = {} # will be replaced with proper functionality later
# configuration file
cherrypy.config.update({
'tools.encode.on': True, 'tools.encode.encoding': 'utf-8',
'tools.decode.on': True,
'tools.trailing_slash.on': True,
'tools.staticdir.root': os.path.abspath(os.path.dirname(__file__)),
})
cherrypy.quickstart(Root(data), '/', {
'/media': {
'tools.staticdir.on': True,
'tools.staticdir.dir': 'static'
}
})
if __name__ == '__main__':
main(sys.argv[1])
步骤 4 - 考虑用户通过表单输入值的应用程序。我们在应用程序中包含两个表单 - index.html 和 submit.html。
步骤 5 - 在上面的控制器代码中,我们有 index() ,这是一个默认函数,如果调用特定的控制器,则首先加载。
步骤 6 - index() 方法的实现可以通过以下方式更改 -
@cherrypy.expose
def index(self):
tmpl = loader.load('index.html')
return tmpl.generate(title='Sample').render('html', doctype='html')
步骤 7 - 这将在启动给定应用程序时加载 index.html 并将其指向给定的输出流。index.html 文件如下 -
index.html
<!DOCTYPE html >
<html>
<head>
<title>Sample</title>
</head>
<body class = "index">
<div id = "header">
<h1>Sample Application</h1>
</div>
<p>Welcome!</p>
<div id = "footer">
<hr>
</div>
</body>
</html>
步骤 8 - 如果要创建一个接受名称和标题等值的表单,则必须在 controller.py 中的 Root 类中添加一个方法。
@cherrypy.expose
def submit(self, cancel = False, **value):
if cherrypy.request.method == 'POST':
if cancel:
raise cherrypy.HTTPRedirect('/') # to cancel the action
link = Link(**value)
self.data[link.id] = link
raise cherrypy.HTTPRedirect('/')
tmp = loader.load('submit.html')
streamValue = tmp.generate()
return streamValue.render('html', doctype='html')
步骤 9 - submit.html 中包含的代码如下 -
<!DOCTYPE html>
<head>
<title>Input the new link</title>
</head>
<body class = "submit">
<div id = " header">
<h1>Submit new link</h1>
</div>
<form action = "" method = "post">
<table summary = "">
<tr>
<th><label for = " username">Your name:</label></th>
<td><input type = " text" id = " username" name = " username" /></td>
</tr>
<tr>
<th><label for = " url">Link URL:</label></th>
<td><input type = " text" id=" url" name= " url" /></td>
</tr>
<tr>
<th><label for = " title">Title:</label></th>
<td><input type = " text" name = " title" /></td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td></td>
<td>
<input type = " submit" value = " Submit" />
<input type = " submit" name = " cancel" value = "Cancel" />
</td>
</tr>
</table>
</form>
<div id = "footer">
</div>
</body>
</html>
步骤 10 - 你将收到以下输出 -
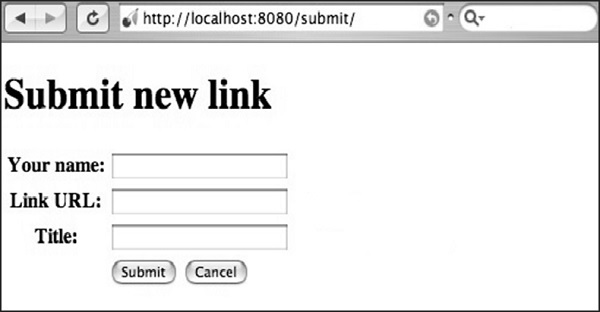
这里,方法名称定义为 POST 。交叉验证文件中指定的方法始终很重要。如果方法包含 POST 方法,则应在适当的字段中在数据库中重新检查这些值。
如果方法包含 GET 方法,则要保存的值将在 URL 中可见。