D3.js - 图表
图表是表示为矩形的二维平面空间。图形具有坐标空间,其中 x = 0, y = 0 坐标位于左下方。根据数学笛卡尔坐标空间,图形的 X 坐标从左到右增加,Y 坐标从下到上增加。
当我们谈论绘制一个 x = 30 和 y = 30 坐标的圆时,我们从左下到右走 30 个单位,然后我们走 30 个单位。
SVG 坐标空间
除了两个重要特征外,SVG 坐标空间的工作方式与数学图坐标空间的工作方式相同 -
- SVG 坐标空间的 x = 0,y = 0 坐标位于左上角。
- SVG 坐标空间的 Y 坐标从上到下增长。
SVG 坐标空间图
当我们谈到在 SVG 坐标空间中绘制一个 x = 30 和 y = 30 坐标的圆时,我们从左上角到右边走 30 个单位,然后向下走 30 个单位。它的定义如下。
var svgContainer = d3
.select("body")
.append("svg")
.attr("width", 200)
.attr("height", 200);
考虑一下,SVG 元素作为 200 单位宽和 200 单位高的图形。我们现在知道 X 和 Y 零坐标位于左上角。我们现在也知道,随着 Y 坐标的增长,它将从图形的顶部移动到底部。你可以设置 SVG 元素的样式,如下所示。
var svgContainer = d3
.select("body").append("svg")
.attr("width", 200)
.attr("height", 200)
.style("border", "1px solid black");
图示例
让我们考虑一下线图的一个例子。
折线图 - 折线图用于显示某些内容的值随时间的变化。它比较了两个变量。每个变量沿轴绘制。折线图具有垂直轴和水平轴。
在这个示例图中,我们可以将 csv 文件记录作为 2006 年至 2017 年的印度国家人口增长。让我们首先创建一个 data.csv 来显示人口记录。
在 D3 文件夹中创建一个新的 csv 文件 -
year,population
2006,40
2008,45
2010,48
2012,51
2014,53
2016,57
2017,62
现在,保存文件并执行以下步骤在 D3 中绘制折线图。让我们详细介绍每一步。
步骤 1 - 添加样式 - 让我们使用下面给出的代码为 line 类添加样式。
.line {
fill: none;
stroke: green;
stroke-width: 5px;
}
步骤 2 - 定义变量 - SVG 属性定义如下。
var margin = {top: 20, right: 20, bottom: 30, left: 50},
width = 960 - margin.left - margin.right,
height = 500 - margin.top - margin.bottom;
这里,第一行定义了四个边距,它们围绕图形所在的块。
步骤 3 - 定义直线 - 使用 d3.line() 函数绘制一条新线,如下所示。
var valueline = d3.line()
.x(function(d) { return x(d.year); })
.y(function(d) { return y(d.population); });
这里,Year 表示 X 轴记录中的数据,而总体表示 Y 轴中的数据。
步骤 4 - 附加 SVG 属性 - 使用以下代码附加 SVG 属性和组元素。
var svg = d3.select("body").append("svg")
.attr("width", width + margin.left + margin.right)
.attr("height", height + margin.top + margin.bottom)
.append("g").attr("transform",
"translate(" + margin.left + "," + margin.top + ")");
在这里,我们附加了组元素并应用了转换。
步骤 5 - 读取数据 - 现在,我们可以从数据集 data.csv 中读取数据。
d3.csv("data.csv", function(error, data) {
if (error) throw error;
}
这里,data.csv 不存在,它会抛出错误。
步骤 6 - 格式化数据 - 现在,使用以下代码格式化数据。
data.forEach(function(d) {
d.year = d.year;
d.population = +d.population;
});
上面的代码确保从 csv 文件中提取的所有值都已正确设置和格式化。每行包含两个值 - 一个值为’year’,另一个值为’population’。该功能一次拉出一行’年’和’人口’的值。
步骤 7 - 设置比例范围 - 格式化数据后,你可以设置 X 和 Y 的比例范围。
x.domain(d3.extent(data, function(d) { return d.year; }));
y.domain([0, d3.max(data, function(d) { return d.population; })]);
步骤 8 - 追加路径 - 追加路径和数据,如下所示。
svg.append("path").data([data])
.attr("class", "line").attr("d", valueline);
步骤 9 - 添加 X 轴 - 现在,你可以使用下面的代码添加 X 轴。
svg.append("g")
.attr("transform", "translate(0," + height + ")")
.call(d3.axisBottom(x));
步骤 10 - 添加 Y 轴 - 我们可以将 Y 轴添加到组中,如下所示。
svg.append("g")
.call(d3.axisLeft(y));
步骤 11 - 工作示例 - 完整代码在以下代码块中给出。创建一个简单的网页 linegraphs.html 并添加以下更改。
graph.html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<script type = "text/javascript" src = "https://d3js.org/d3.v4.min.js"></script>
<style>
.line {
fill: none;
stroke: green;
stroke-width: 5px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<script>
// set the dimensions and margins of the graph
var margin = {top: 20, right: 20, bottom: 30, left: 50},
width = 960 - margin.left - margin.right,
height = 500 - margin.top - margin.bottom;
// set the ranges
var x = d3.scaleTime().range([0, width]);
var y = d3.scaleLinear().range([height, 0]);
// define the line
var valueline = d3.line()
.x(function(d) { return x(d.year); })
.y(function(d) { return y(d.population); });
// append the svg obgect to the body of the page
// appends a 'group' element to 'svg'
// moves the 'group' element to the top left margin
var svg = d3.select("body").append("svg")
.attr("width", width + margin.left + margin.right)
.attr("height", height + margin.top + margin.bottom)
.append("g").attr("transform",
"translate(" + margin.left + "," + margin.top + ")");
// Get the data
d3.csv("data.csv", function(error, data) {
if (error) throw error;
// format the data
data.forEach(function(d) {
d.year = d.year;
d.population = +d.population;
});
// Scale the range of the data
x.domain(d3.extent(data, function(d) { return d.year; }));
y.domain([0, d3.max(data, function(d) { return d.population; })]);
// Add the valueline path.
svg.append("path")
.data([data])
.attr("class", "line")
.attr("d", valueline);
// Add the X Axis
svg.append("g")
.attr("transform", "translate(0," + height + ")")
.call(d3.axisBottom(x));
// Add the Y Axis
svg.append("g")
.call(d3.axisLeft(y));
});
</script>
</body>
</html>
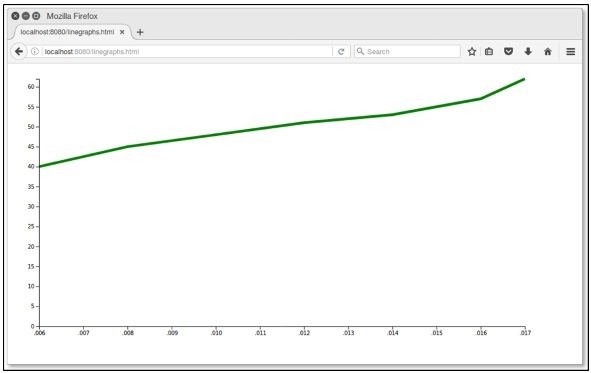
现在请求浏览器,我们将看到以下结果。